The acceleration of free falling objects is called the acceleration due to gravity since objects are pulled towards the center of the earth.
Value of acceleration for a marble in free fall.
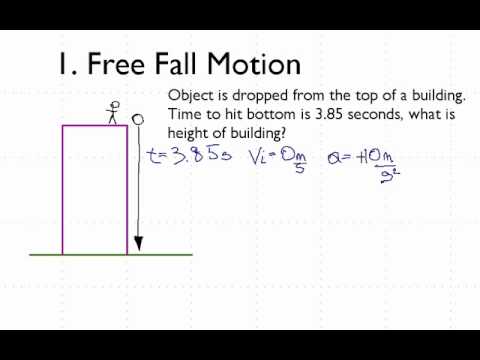
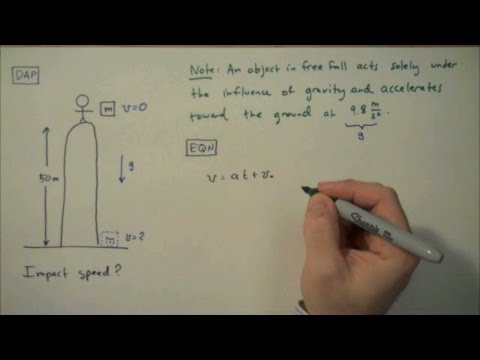
This force causes all free falling objects on earth to have a unique acceleration value of approximately 9 8 m s s directed downward.
Watch your precision please report your values in the table above to the appropriate precision.
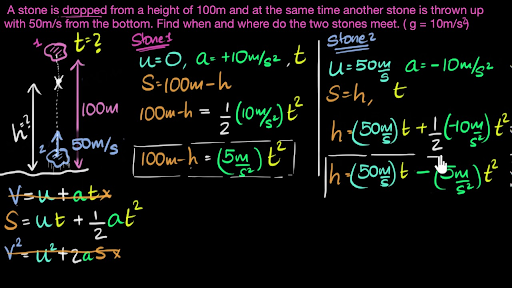
Use g 10m s2 and factor the quadratic or use the quadratic formula.
This acceleration value is commonly called g.
In reality though a falling object s velocity is constrained by a value called the terminal velocity.
In the customary system of units g 32 ft s 2 or about 22 mi hr s.
Create a graph to show the linearized relationship between the distance fallen and the time to fall for the steel marble.
Such an object will experience a downward acceleration of 9 8 m s s.
Acceleration of the object a 9 8 m s2 b.
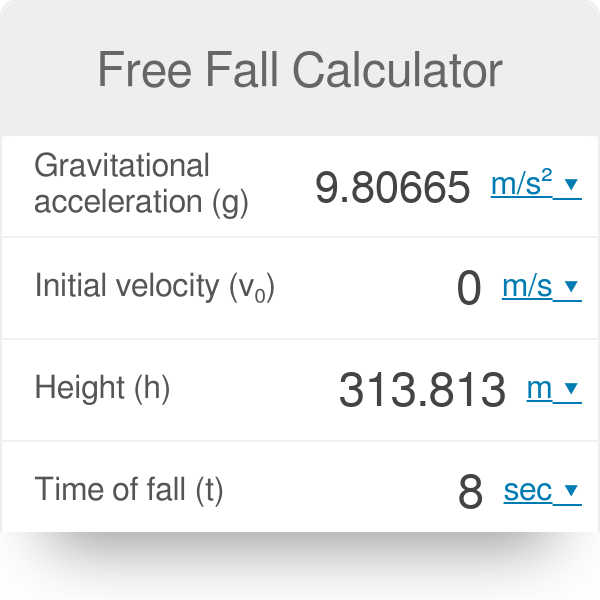
Without the effect of air resistance each object in free fall would keep accelerating by 9 80665 m s approximately equal to 32 17405 ft s every second.
Free falling objects are falling under the sole influence of gravity.
The objective of this lab is to drop a marble from different heights record the data and then predict how long it will take to hit the ground from the final height.
A ball is thrown downward with an initial speed of 20 m s on earth.
Marble falls 0 005 m time for the marble to fall 0 0002 s trial 1 trial 2 trial 3 note.
Falling time a to b s 1.
Gis the free fall acceleration expressed in m s or ft s.
Falling marble data trial explore b2 speed acceleration and free fall gravity drop what does a graph of the motion of a falling marble look like.
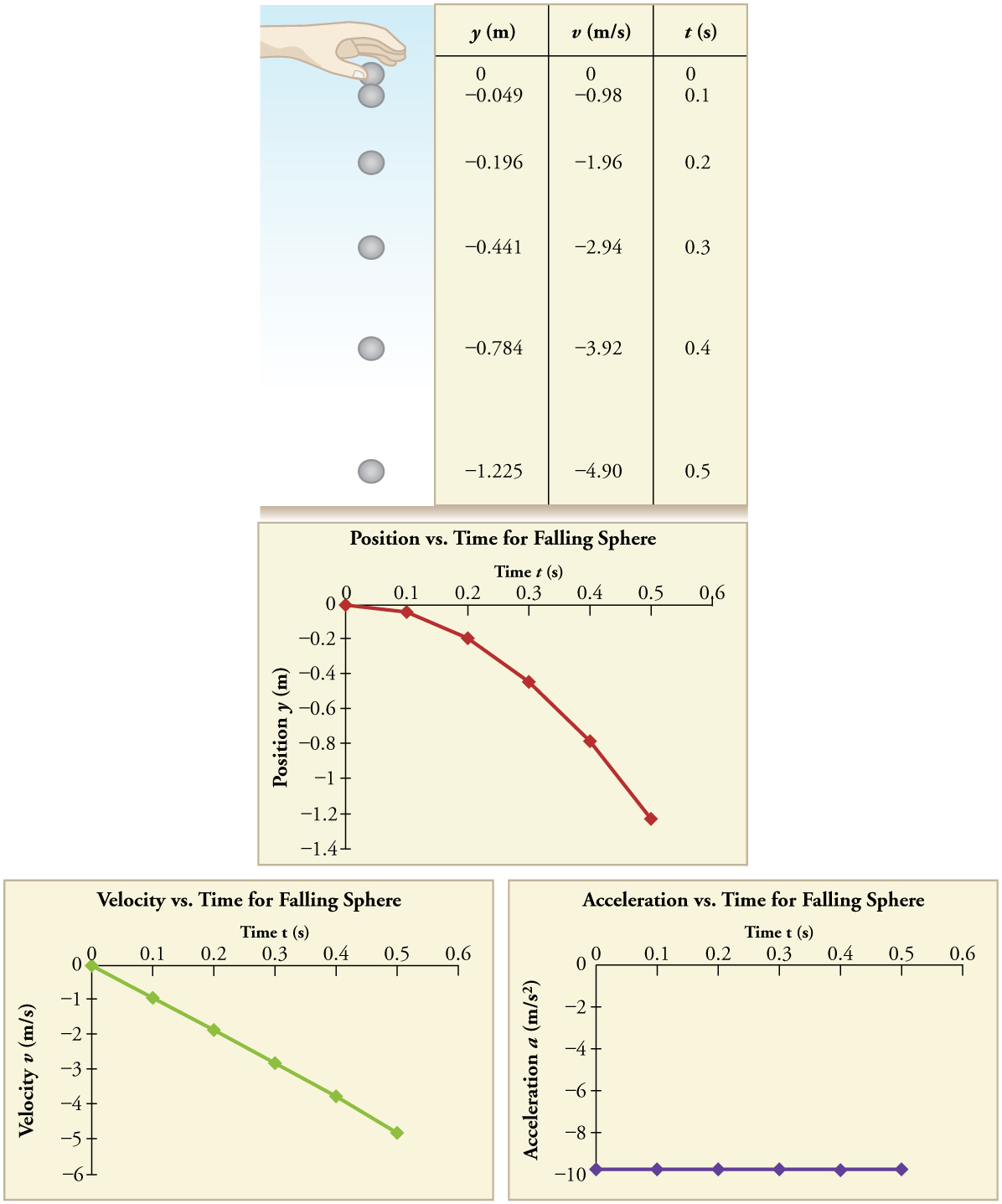
The acceleration due to gravity is constant on the surface of the earth and has the value of 9 80 m s2 m s 2.
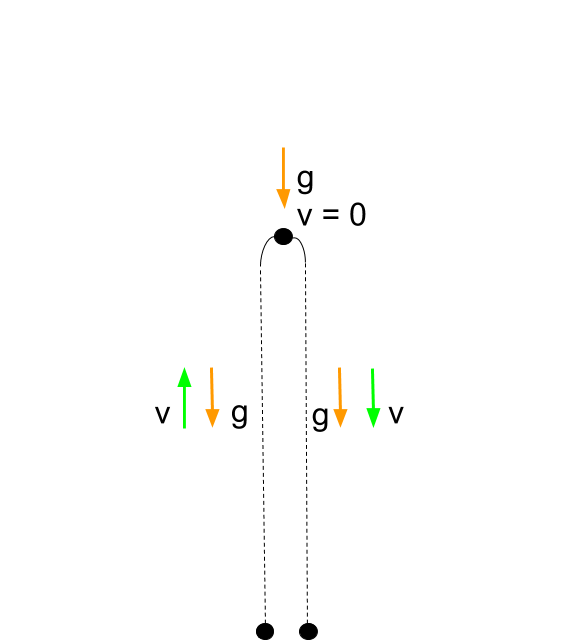
Whether the object is falling downward or rising upward towards its peak if it is under the sole influence of gravity then its acceleration value is 9 8 m s s.
Time required to fall 300 m hint.
The acceleration of a freely falling object any freely falling object near the surface of the earth is about 9 8 m s 2 which is conveniently close to 10 m s 2 for rough calculations.
Near earth where g 9 8 m s 2 the acceleration of a free falling body is a g 1 d w g 1 kv 2 w where w mg is the weight of the body with mass m.
As you can see the acceleration has.
Marble drop lab purpose.
Like any moving object the motion of an object in free fall can be described by four kinematic equations.
Time required to reach a speed of 50 m s gt t d.
We refer to this special acceleration as the acceleration caused by gravity or simply the acceleration of gravity.
Free fall with non zero v o 3.